Description
Daymet Science and Introduction
Daymet is a data product derived from a collection of algorithms and computer software designed to interpolate and extrapolate from daily meteorological observations to produce gridded estimates of daily weather parameters. Weather parameters generated include daily surfaces of minimum and maximum temperature, precipitation, vapor pressure, radiation, snow water equivalent, and day length produced on a 1 km x 1 km gridded surface. The motivation for producing Daymet is to provide measurements of near-surface meteorological conditions where no instrumentation exists. Having estimates of these surfaces is critical to understanding many processes in the terrestrial biogeochemical system.
Development of current versions of Daymet as well as its curation and distribution are supported by funding from NASA through the Earth Science Data and Information System ( ESDIS ) and the Terrestrial Ecology Program. The continued development of the Daymet algorithm and processing is also supported by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research within the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
| Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Years Available | Spatial Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1km x 1km | Daily | 1980 - present calendar year | North America, Hawaii |
| 1km x 1km | Daily | 1950 - present calander year | Puerto Rico* |
Inputs
Required model inputs include a digital elevation model, derived horizon files, a land water mask, and observations of daily maximum temperature, minimum temperature, and precipitation from ground-based meteorological stations. For Daymet version 3 processing, surface observations were available from the Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN)-Daily dataset distributed by the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) (Menne et al., 2012). One file per year for each year of station data is assembled and input into the Daymet model algorithm.
A Daymet dataset product is available for the the station-level daily weather observation data and the corresponding Daymet model predicted data for the three model parameters: tmin, tmax, and prcp. Also included are corresponding station metadata files for each variable and year, including the station name, station identification, latitude, and longitude.
Processing
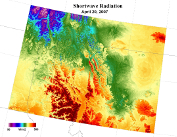
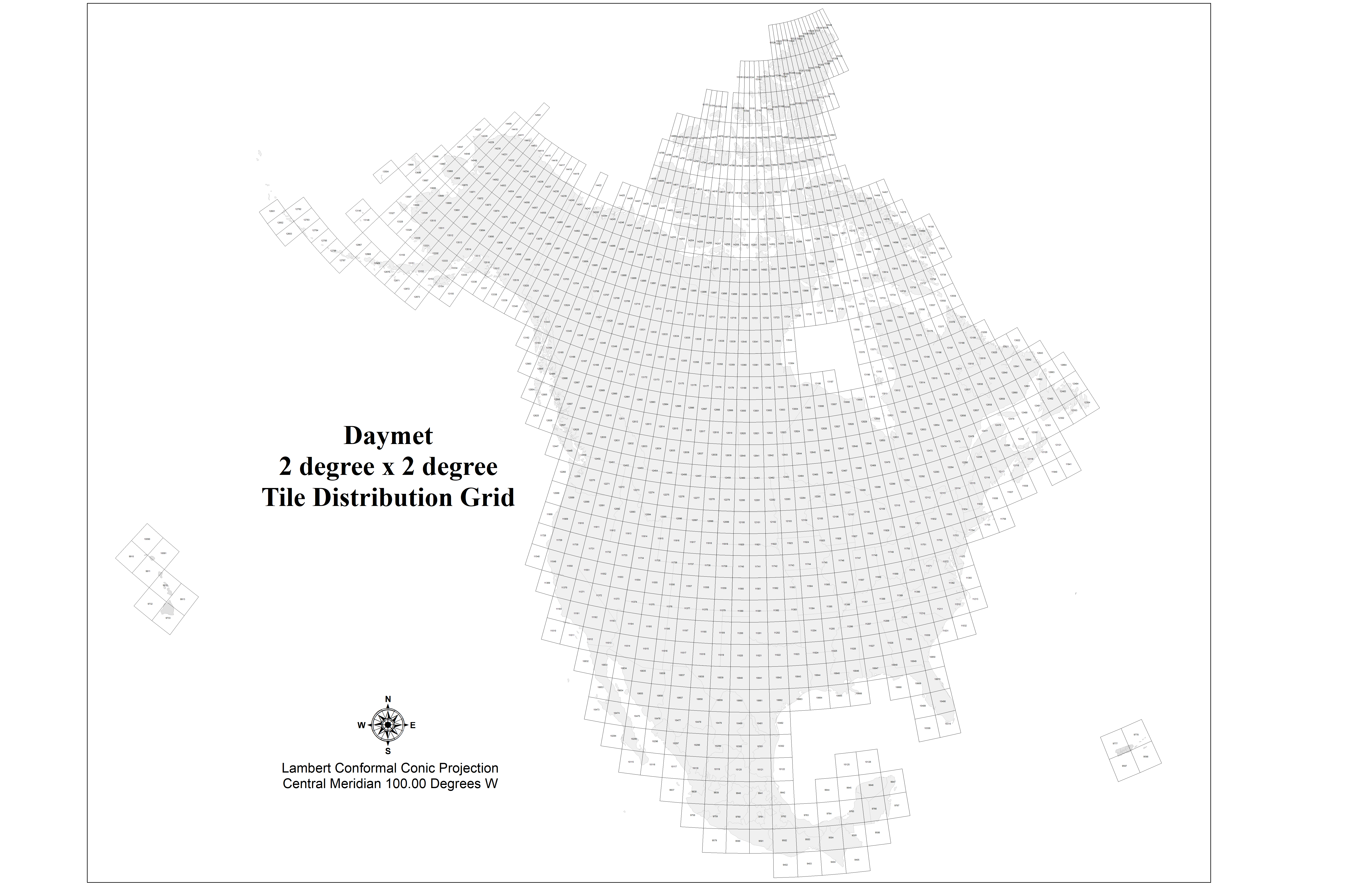
Shortwave Radiation in Northern Idaho / Western Montana (April 27, 2007) . Mosaic of 8 2-degree Daymet processing tiles
The Daymet algorithm manages the large number of input data and large spatial extent of the study area by creating a system of 2 degree x 2 degree tiles which are processed individually through the Daymet software. These tiles are identified by a TileID which is derived within the Daymet algorithm and is consistent throughout the temporal period of the Daymet record.
The Daymet approach to estimating daily surface weather parameters at locations lacking instrumentation is based on a combination of interpolation and extrapolation, using inputs from multiple instrumented sites and weights for each site that reflect the spatial and temporal relationships of the estimation location to the instrumental observations. The approximate number of instrumental observations to use for each estimation is defined as a parameter for each of the primary Daymet variables. As part of a series of algorithm modifications intended to improve robustness in regions of very low station density, the Daymet V4 algorithm drops the iterative station density calculation and instead defines a search radius for each estimation location which is sized to capture exactly the average number of input stations, based on pre-calculated arrays of station distances. Given the pre-processed input station observations and the pre-calculated station lists and interpolation weights for each location in the estimation grid, two separate workflows are used to produce the primary Daymet output variables: one for the daily temperature variables (Tmax and Tmin) and another for the daily precipitation variable (Prcp).
In addition to daily maximum and minimum temperature and daily total precipitation, the Daymet data record includes estimates of other important surface weather quantities that are not routinely observed, or are available as observations from only a small fraction of the temperature and precipitation observing stations. These secondary output variables are daily total shortwave radiation (Srad), daily average water vapor pressure (VP), duration of the daylight period (daylength), and a simple estimate of accumulated snowpack, measured as snowpack water equivalent (SWE). The daylength estimate is based on geographic location and time of year. Estimates for the other secondary variables (Srad, VP, and SWE) are derived from the primary temperature and precipitation variables on the basis of theory and empirical relationships, as further described in Thornton et al. 2020.
Model Outputs and Data Products
For ORNL DAAC distribution, Daymet binary outputs are converted to a spatially referenced, gridded, netCDF file format that follow netCDF Climate and Forecast (CF) Metadata conventions. The CF standard provides a description of each data variable represented, and the spatial and temporal properties of each 2-degree tile. By providing data in this format, users have a robust means to locate data in both space and time as well as a number of software options for their own research needs. Daily gridded surface data for each of the 7 variables are listed below. The ORNL DAAC also mosaics the 2-degree tiles into a seamless gridded netCDF file of daily data for each variable and each year. These mosaic files, and other pre-derived data products, are available for download through the ORNL DAAC.
Parameters, Parameter abbreviations, Units, and Descriptions:
| Parameter | Abbr | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day length | dayl | s/day | Duration of the daylight period in seconds per day. This calculation is based on the period of the day during which the sun is above a hypothetical flat horizon |
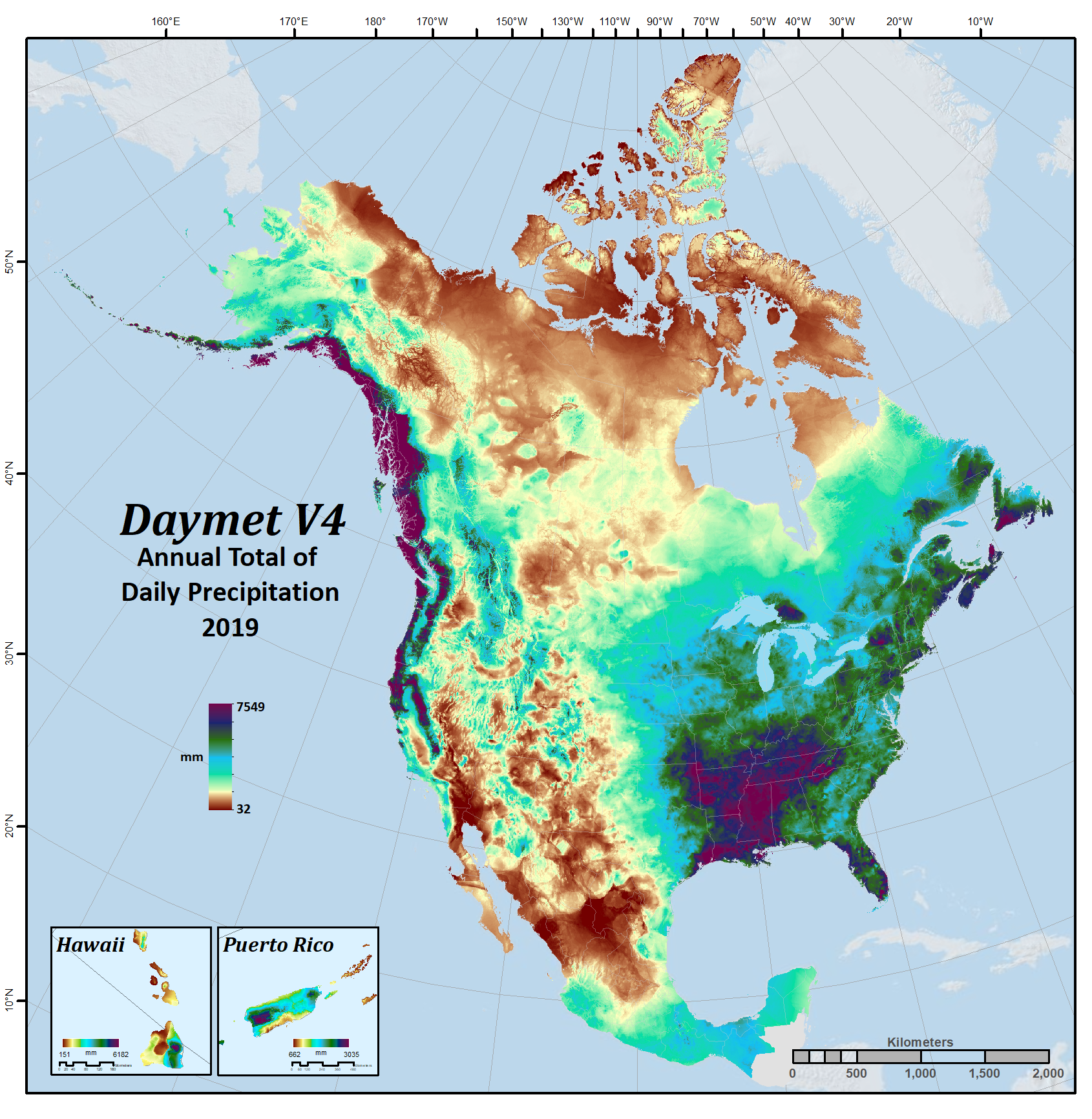
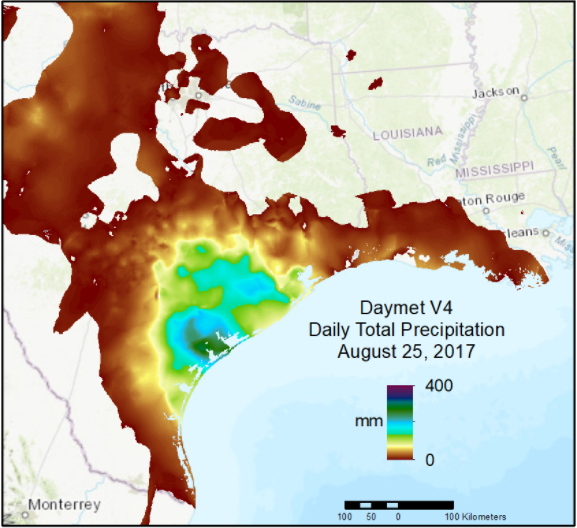
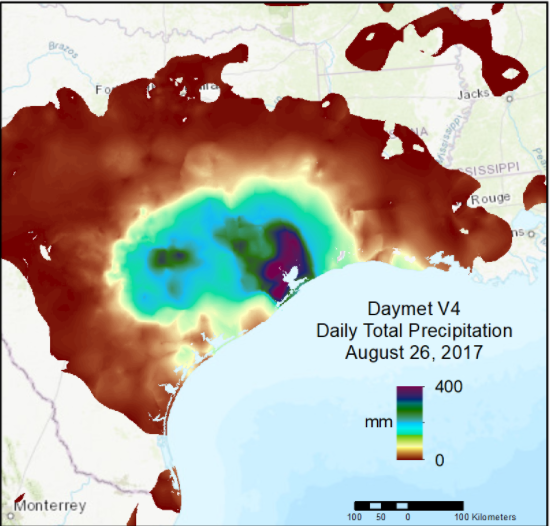
| Precipitation | prcp | mm/day | Daily total precipitation in millimeters per day, sum of all forms converted to water-equivalent. Precipitation occurrence on any given day may be ascertained. |
| Shortwave radiation | srad | W/m2 | Incident shortwave radiation flux density in watts per square meter, taken as an average over the daylight period of the day. NOTE: Daily total radiation (MJ/m2/day) can be calculated as follows: ((srad (W/m2) * dayl (s/day)) / l,000,000) |
| Snow water equivalent | swe | kg/m2 | Snow water equivalent in kilograms per square meter. The amount of water contained within the snowpack. |
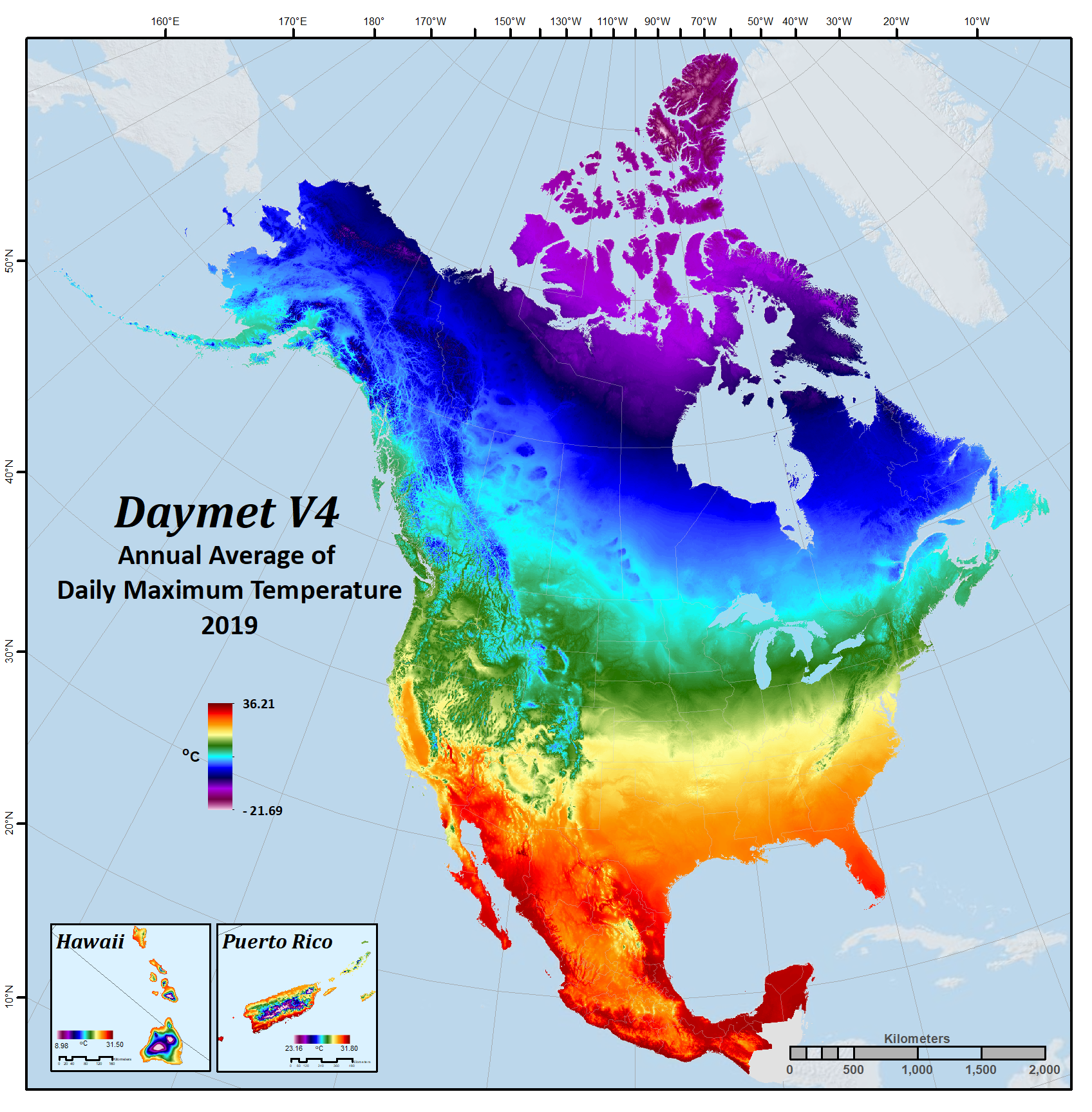
| Maximum air temperature | tmax | degrees C | Daily maximum 2-meter air temperature in degrees Celsius. |
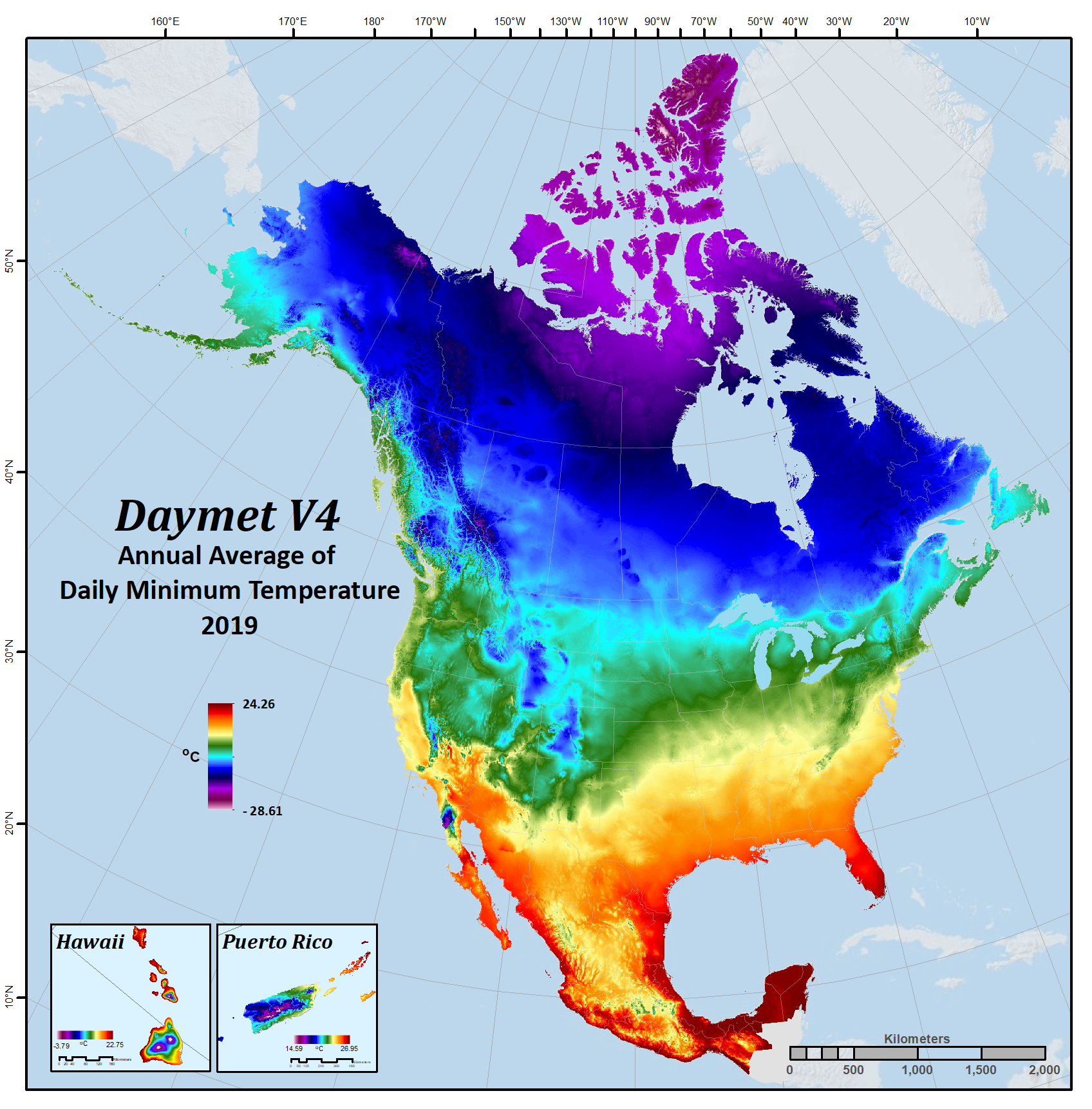
| Minimum air temperature | tmin | degrees C | Daily minimum 2-meter air temperature in degrees Celsius. |
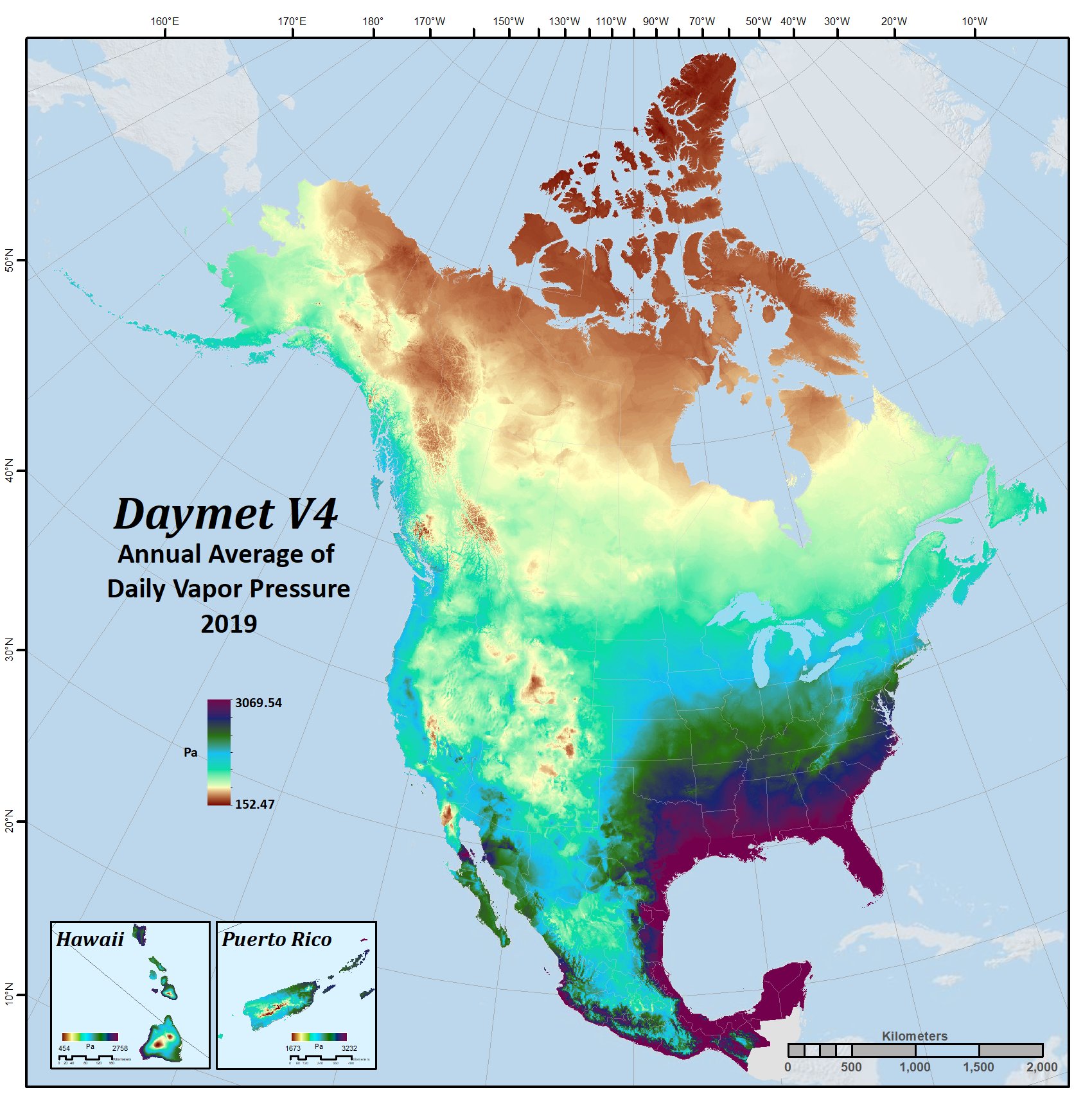
| Water vapor pressure | vp | Pa | Water vapor pressure in pascals. Daily average partial pressure of water vapor. |
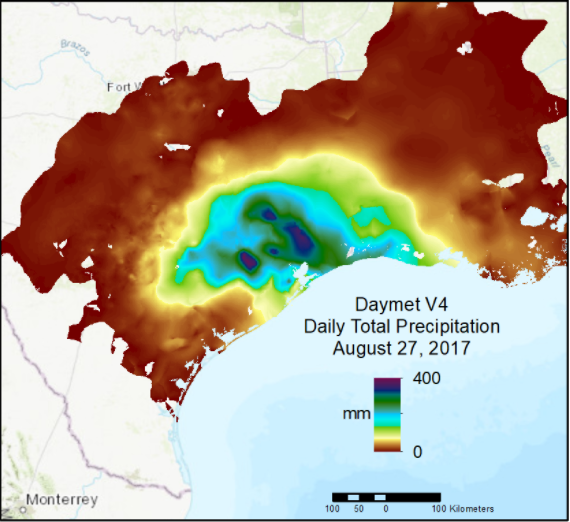
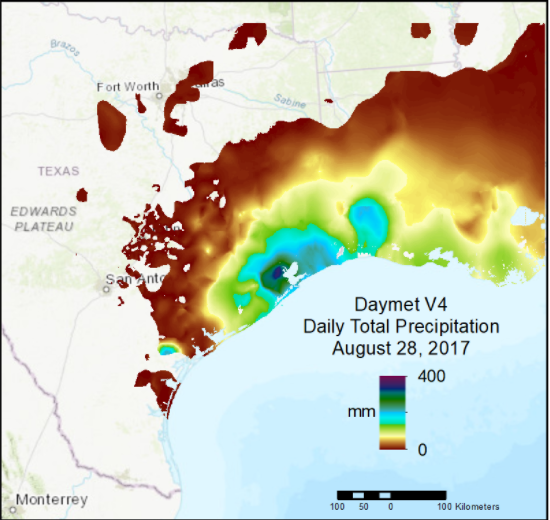
Daymet Daily Data:
|
|
|
|
|
Daymet Annual Climatologies
Version Information
The Daymet dataset is stored and distributed as individual CF-Compliant netCDF file for each Daymet variable. The most current Daymet data is being delivered to the user in terms of both Daymet software and Daymet data versions. Version information is recorded in the header file of each of the CF-netCDF files within the Global Attribute fields; Version_software and Version_data. All Daymet data is provisional and subject to revision.
Projection Definition
The North American Daymet projection system and parameters:
- Projection System: Lambert Conformal Conic
- Parameters:
- projection units: meters
- datum (spheroid): WGS_84
- 1st standard parallel: 25 deg N
- 2nd standard parallel: 60 deg N
- Central meridian: -100 deg (W)
- Latitude of origin: 42.5 deg N
- false easting: 0
- false northing: 0
The spatial resolution of the Daymet gridded dataset is 1 km.
Calendar
The Daymet calendar is based on a standard calendar year. All Daymet years have 1 - 365 days, including leap years. For leap years, the Daymet database includes leap day. Values for December 31 are discarded from leap years to maintain a 365-day year.